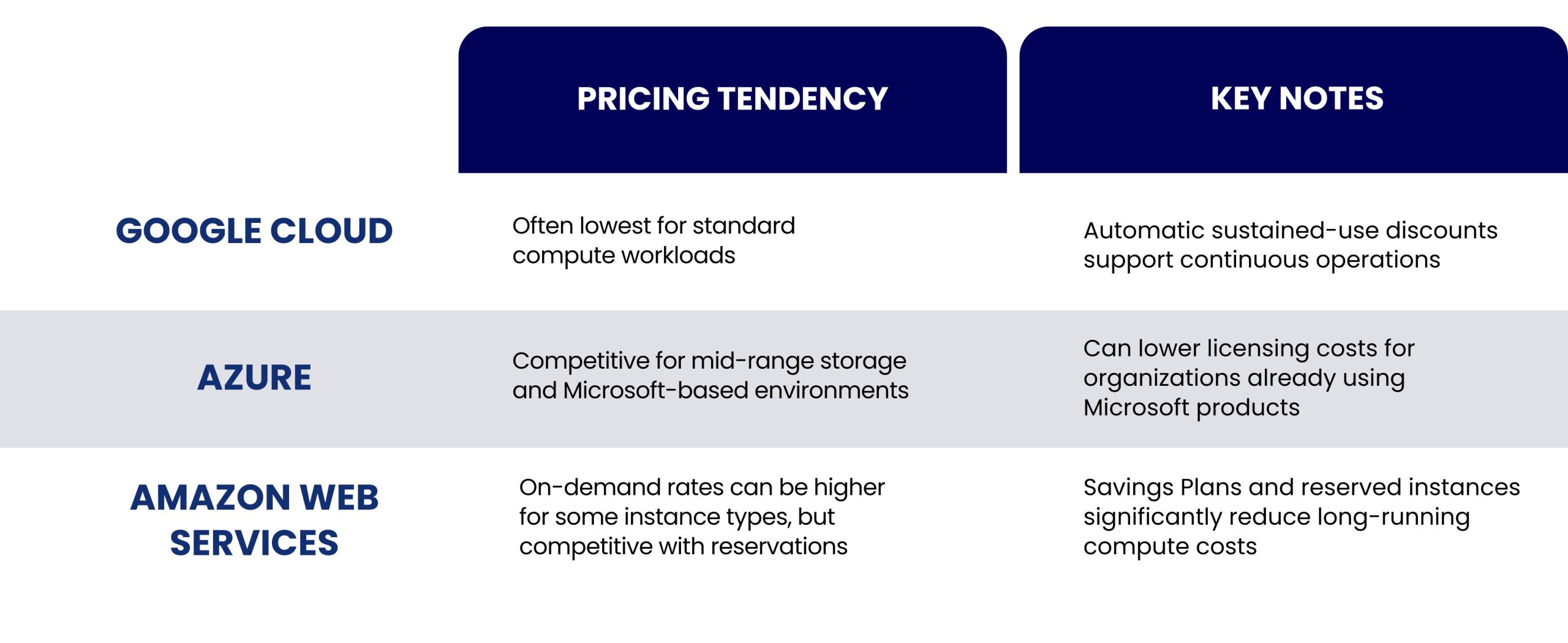
Amazon Web Services launched in 2006 and became the first major provider to offer cloud infrastructure as an on-demand utility in a pay-as-you-go model. It provides a large portfolio of services for computing, storage, networking, security, and application deployment, all designed to scale as business needs grow. Organisations use it to build and run applications without owning physical hardware, which reduces maintenance overhead and supports faster experimentation.
AWS cloud computing is known for its extensive documentation, strong ecosystem of solution partners, and reliable global network of data centers. This makes it suitable for enterprises that prioritize availability, regional redundancy, and the flexibility to expand into new markets or product lines with minimal operational disruption.
What is Microsoft Azure?
Microsoft Azure launched in 2010 and is tightly integrated with Microsoft’s core enterprise software environment. It offers services across compute, storage, identity, data platforms, analytics, and security, providing a foundation for both traditional and cloud-native applications.
Organizations that already use Microsoft technologies often find Azure appealing because it can extend existing authentication systems, governance frameworks, and development workflows into the cloud without major restructuring.
Azure also supports hybrid deployments, allowing businesses to gradually modernize applications while keeping certain workloads on-premise when required. This approach helps companies maintain stability during transitions and adopt cloud capabilities at their own pace. Azure’s strong management and monitoring tools support centralized oversight across distributed environments.
What is Google Cloud Platform (GCP)?
Google Cloud Platform was built on the same global infrastructure that powers Google’s search, communication, and content services. It provides cloud capabilities in computing, storage, networking, application development, and high-performance data processing.
GCP has a reputation for strong analytics performance and efficient handling of distributed workloads, making it a compelling choice for organizations working with large datasets or advanced data modelling. It also offers a developer-friendly environment that encourages containerized and microservices-based application design.
Teams that value open-source tooling and modern architecture patterns often gravitate toward GCP because of its support for agile development practices and streamlined operational workflows. This enables faster iteration cycles and scalable deployment models for data-driven platforms.